Yet with the global sharing of digital replicas comes the challenge of managing attribution. “In an evolving digital culture, it may be that organizations embrace more making their digital resource collections available on an open access basis, particularly if it becomes harder and harder to regulate use,” said Anisha Birk, an associate at Farrer & Co. in London. Open access broadens engagement, promoting creativity, public benefit, and simplified academic use with fewer licensing restrictions.
“However, while digital resources can be a potential revenue source, the profitability remains uncertain due to the costs associated with maintaining a picture library,” Birk said. Notably, users can also use the materials for secondary creation, and the resulting works can become new digital resources. If used commercially, creators can share the profits with the copyright holders.
“This enriches the content and provides a platform for sharing and co-creating works using digital resources, fostering a healthy creative ecosystem,” said Xiaohong Ding, the deputy director of the Digitalization Research Institute at the Dunhuang Academy, in an article by Xinhua News.
Open access presents a transformative opportunity for the dissemination of knowledge, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. While digital resources can generate significant revenue potential through various models, the costs associated with maintaining and updating digital libraries can be substantial. This includes expenses related to technology infrastructure, content curation and ongoing support for users.
Moreover, digital materials often inspire secondary creations – such as adaptations, remixes and scholarly analyses – which enrich the cultural and academic ecosystem. These secondary works not only enhance the original content but also foster a collaborative environment where creativity can flourish.
Since its launch in late 2022, the Digital Dunhuang Open Material Library has seen impressive engagement, with over four million views and 30,000 downloads. This indicates a strong interest in the resources it offers, highlighting the library’s role in making cultural heritage accessible to a global audience.
Reimagining the museum experience
The works of Dunhuang Academy take digital preservation to new heights, using high-definition scanning, advanced game engines, dynamic lighting and cloud gaming to create an astonishingly immersive experience. This digital reconstruction offers high-resolution replicas of notable sites, including the Mogao Caves’ cliff faces and detailed replicas of specific caves. Users can explore these lifelike recreations on a WeChat mini-program, experiencing the timeless artistry of Dunhuang with movie-quality visuals.
Popular tourist sites in Dunhuang are now using VR and AR technology to turn visitors from passive spectators into active participants, creating a dynamic blend of history and modern innovation. The Exploring Dunhuang – Digital Immersive Exhibition, a collaboration between the Dunhuang Academy and Tencent, allows visitors to don VR headsets and immerse themselves in the ancient world of Dunhuang’s murals. At Mingsha Mountain and Crescent Lake, an 8K VR flight experience lets visitors “soar” over Dunhuang, providing an awe-inspiring virtual journey with no transportation needed.
Another immersive highlight, Dunhuang Unbound: Secret Treasures and Desert Sands, has quickly become a tourist favourite since its debut on September 10 in Dunhuang City. Using advanced spatial positioning, multi-user interaction and real-time rendering, this project reconstructs the Tang Dynasty city of Shazhou, allowing visitors to step back in time in a highly interactive setting. Participants become part of the storyline, moving through the experience as first-person characters in an adventurous treasure hunt. This role-play deepens their connection with Dunhuang’s vibrant history and culture.
Located in the Shazhou Yijing Digital Aesthetics Space, a hub for digital cultural tourism, Dunhuang Unbound is part of a broader array of VR experiences, including Dunhuang Manuscripts, Han Bamboo Slips of Dunhuang, and Beyond Time Exploration. These projects skillfully weave technology and art, offering visitors an unparalleled opportunity to explore the enduring charm of Dunhuang.
Copyright and ownership in the digital age of cultural preservation
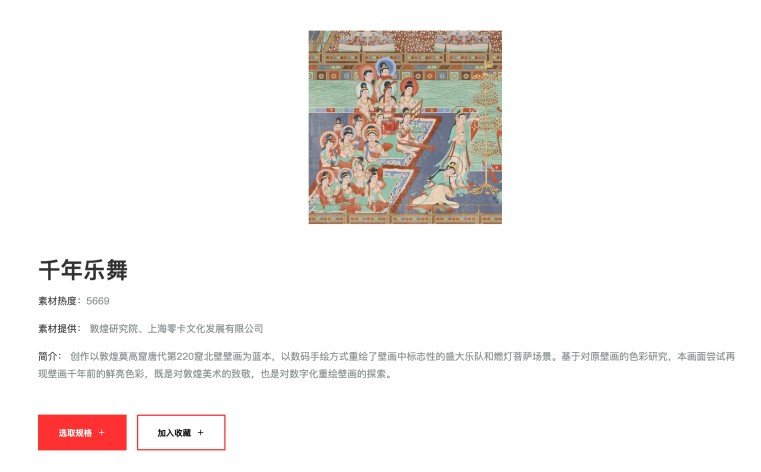
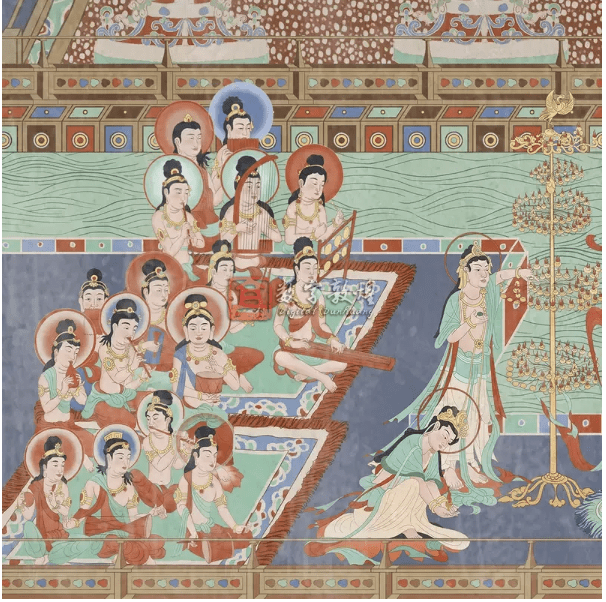
Beyond mere replicas, Digital Dunhuang collaborates with companies to recreate vibrant murals based on original designs, capturing the brilliance of ancient artworks through rigorous colour studies. Although these digital resources primarily serve educational purposes, their profound cultural value raises thought-provoking questions for intellectual property scholarship.